We hunt six stunning planetary nebulae, the beautiful swan song of dying stars
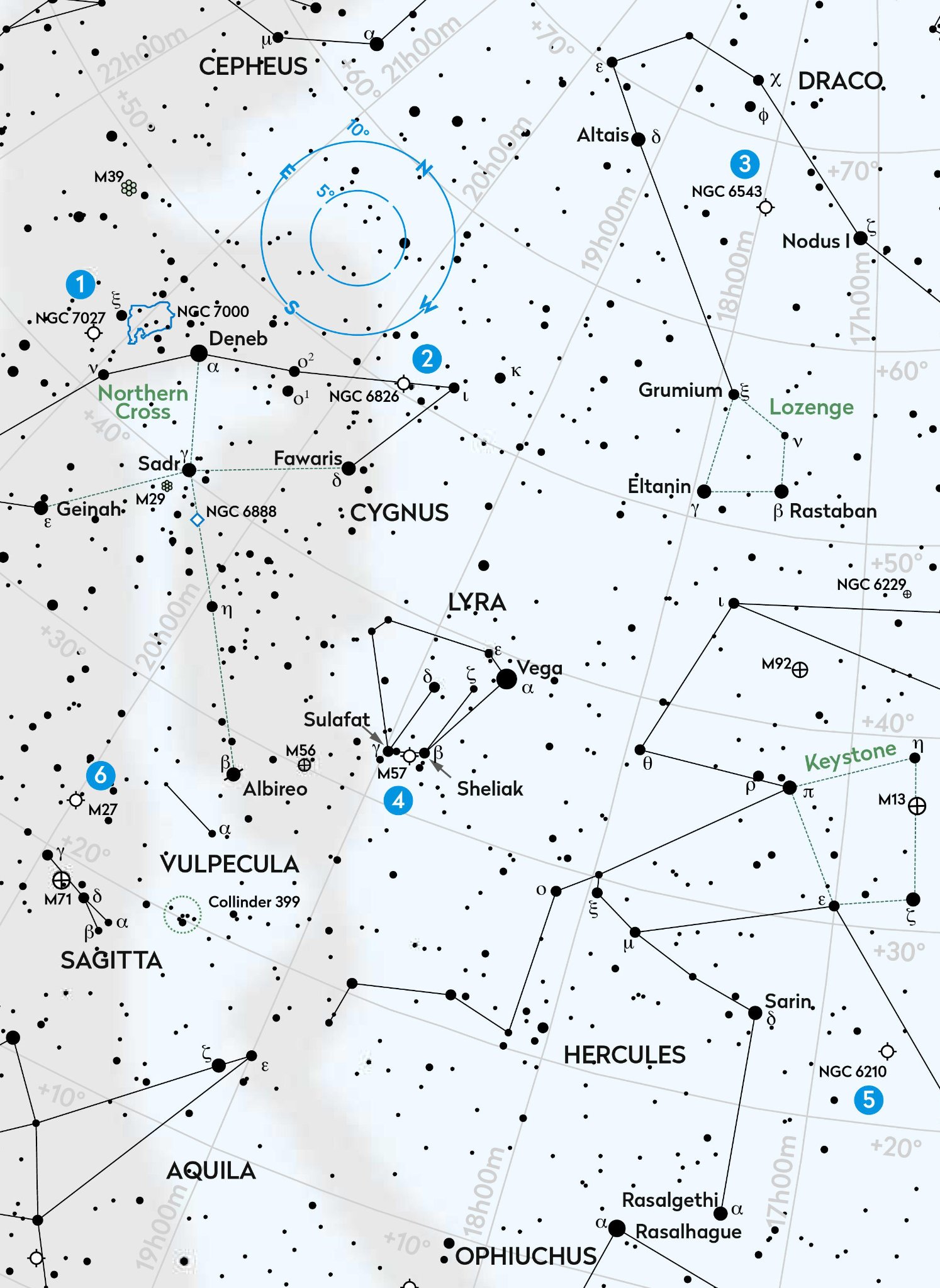
1. NGC 7027
Recommend equipment: Small/medium or large telescope
Let’s start with NGC 7027, a 10th-magnitude planetary nebula in Cygnus. It’s located within the busy Milky Way, 5.5° southeast of Deneb, 2.1° east-northeast of mag. +3.9 Nu (ν) Cygni. Known as the Jewel Bug Nebula, it’s around 3,000 lightyears away and being a youthful and rare proto-planetary nebula, is small at 0.2 x 0.1 lightyears across. It appears 14 arcseconds across. Small telescopes reveal an object like a star at low and medium powers. A high magnification hints at an extended oval shape through smaller scopes, appearing more rectangular through larger instruments.
2. NGC 6826
Recommend equipment: Small/medium or large telescope
We move towards the tip of Cygnus’s northwestern wing for our next target, the Blinking Nebula, NGC 6826. The name reflects a common property of some planetary nebulae. Using direct vision through smaller apertures, a bright central star causes the fainter nebula to disappear from view. However, using averted vision the nebula blinks into view again. Look for NGC 6826 along the line from Deneb (Alpha (α) Cygni) towards Iota (ι) Cygni. It lies 2.6° from Iota. The nebula has an integrated magnitude of +8.8 and a total apparent size of 27 x 24 arcseconds. The central star shines at mag. +10.4.
3. NGC 6543
Recommend equipment: Small/medium or large telescope
Located 21° northwest of the Blinking Nebula is another famous planetary nebula known as the Cat’s Eye Nebula, NGC 6543. This one is found within a loop of the snake-like body of Draco, the Dragon, 7.2° west of mag. +3.1 Altais (Delta (δ) Draconis). Shining at mag. +9.8, with an apparent diameter of 20 arcseconds, it’s visible through smaller scopes as an elongated smudge. If you have steady seeing and a scope over 200mm, try using a high magnification in conjunction with averted vision to see whether you can detect any of the faint, intricate detail in the inner regions of the nebula. The Cat’s Eye Nebula’s central star shines at mag. +11.4.
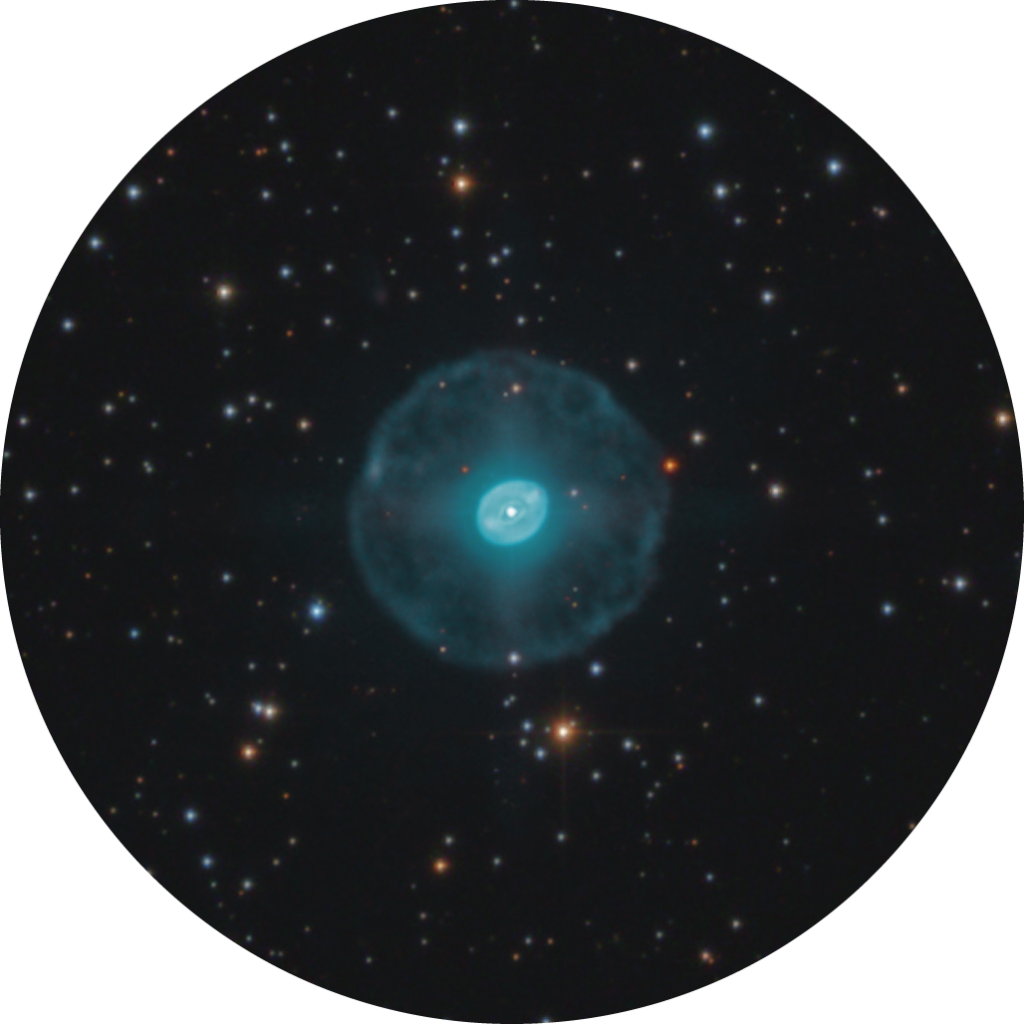

4. M57
Recommend equipment: Small/medium or large telescope
Our next target is easy to find using the bright star Vega (Alpha (α) Lyrae), which forms the top edge of the large Summer Triangle asterism with Deneb. South of Lyra is a squashed-diamond pattern with Sheliak and Sulafat (Beta (β) and Gamma (γ) Lyrae respectively) at the southern edge. The famous Ring Nebula, M57, sits three-fifths of the way from Sulafat towards Sheliak, fractionally south of the line joining both stars. At low power and despite its 1.3-arcminute size, this mag. +9.7 planetary nebula can easily be overlooked as a star, but larger magnification reveals its extended oval shape. A 150mm or larger scope will show a darker patch inside the oval, the feature that produces its ring-like appearance. M57’s central star is faint, shining at mag. +14.7.
5. NGC 6210
Recommend equipment: Small/medium or large telescope
For mag. +9.3 NGC 6210, we head west from Lyra to find the dim but distinctive Keystone asterism in Hercules. Identify the eastern side, marked by mag. +3.2 Pi (π) and +3.9 Epsilon (ε) Herculis. Extend the line from Pi through Epsilon 1.2 times that distance to arrive at NGC 6210. Although it’s small with an apparent diameter of 16 arcseconds, its surface brightness is relatively high – an ideal target for smaller scopes which reveal it to look like a small blue-green disc. Don’t be afraid to pile on the power. An OIII or UHC filter may reveal extra outer detail through larger scopes. The central star for this nebula shines at mag. +12.7.
6. M27
Recommend equipment: Small/medium or large telescope
Finally, the spectacular Dumbbell Nebula, M27, in Vulpecula. It’s easy to locate. Head back to Lyra and then to Cygnus. Extend the line from Sulafat through Albireo (Beta (β) Cygni) for the same distance again and you’ll arrive at the nebula. It shines with an integrated magnitude of +7.4 and has impressive overall apparent dimensions of 8 x5.6 arcminutes. A small scope will reveal its apple-core, pinched-waist appearance. An OIII filter works really well, revealing uneven textures. The two lobes are of unequal brightness, the southern one appearing smaller and brighter. A 300mm or larger scope should reveal the mag. +13.8 central star.